Bus Topology
As a solution, the two endpoints of the bus are normally terminated with a device called a that prevents this reflection. Distributed bus [ ] The type of network topology in which all of the nodes of the network are connected to a common transmission medium which has more than two endpoints that are created by adding branches to the main section of the transmission medium – the physical distributed bus topology functions in exactly the same fashion as the physical linear bus topology (i.e., all nodes share a common transmission medium). Star network topology In local area networks with a star topology, each network host is connected to a central hub with a point-to-point connection. So it can be said that every computer is indirectly connected to every other node with the help of the hub.
A network topology is the physical layout of computers, cables, and other components on a network. There are a number of different network topologies, and a network may be built using multiple topologies. The different types of network layouts are Bus topology, Star topology, Mesh topology, Ring topology, Hybrid topology and Wireless topology. Nfs most wanted apk data. This lesson explains what is bus topology. Short Bytes: In this article, you’ll know what is bus topology, what are its types, how communication and data packet happens on a bus topology. We’ll also tell you what are the advantages.
A star network is a topology of the local network where a central workstation is connected with each end-user computer or peripherals. A tree structure means that, the central nodes of these star networks are linked to a main cable (the Bus topology). So, a Tree network topology is a few Star networks connected into a Bus topology. This scheme can be applied to draw the particular physical or logical network diagrams using the ConceptDraw Computer and Networks solution. Network Diagram Examples When studying computer science, it is important to have good training manuals. To understand how the networks and data links work, you will probably need a set of network diagram examples depicting all the possible interconnections between network devices. You can find them on Internet or try to create your own.
Hubs are sometimes called concentrators. Next lesson In the next lesson, you will learn about the characteristics of the ring topology. © DigitalThink, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
For those who need a temporary network that can be setup quickly, there isn’t a better option that is available right now. If several users need mutual access to a printer, adding the printer to the network meets that need immediately.
Best Topology For A Business
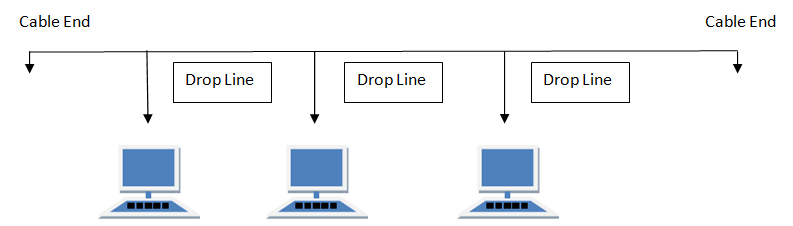
Contents • • • • • • Function [ ] A on a bus network is called a Station or workstation. In a bus network, every station will receive all network traffic, and the traffic generated by each station has equal transmission priority. A bus network forms a single. In order for nodes to transmit on the same bus simultaneously, they use a technology such as (CSMA) or a.
In comparison,, common in vehicles, are primarily distributed networks of one or more controllers interconnected with sensors and actuators over, invariably, a physical bus topology. Diagram of different network topologies. Two basic categories of network topologies exist, physical topologies.
Also bus network topology within networks are simpler to extend by joining cable with connector or repeater. Any of the existing bus network topologies work better for small networks which can be also a disadvantage in case yours is quite large. Other disadvantages are: large amount of packet collisions on one network which results in high amounts of packet loss and the possibility of the network to be shut down in case there is a break in the main cable or in case one of the T connectors breaks. But, again, the good thing is that in this topology data being transferred may be accessed by any workstation. There are two types of the bus network topologies, one of which is a “Linear bus” one. This type of network topology is the one where all of the nodes of the entire network are connected to one common transmission with only two endpoints.
Shortest Path Bridging will replace Spanning Tree in the Ethernet fabric. Tech Power Up. Retrieved 11 May 2012. Fedyk, Ed.,; P. Ashwood-Smith, Ed.,; D. Unbehagen (April 2012). Retrieved 12 May 2012.
But, again, the good thing is that in this topology data being transferred may be accessed by any workstation. There are two types of the bus network topologies, one of which is a “Linear bus” one.
It allows you to connect many different points using just one central one. Like anything in technology, there are good things and there are bad things that can come from it’s use. Advantages of Bus Topology 1. Manageable It is very easy to identify problems and fix them quickly and efficiently using bus topology. This is because everything is connected together. Inexpensive The equipment and cables that are needed to set up this form of network are very minimal.
Communication between any two given devices is possible, but might require an intermediary connection. Full mesh topologies are usually impractical because the number of connections increases dramatically with every new node added to the network. However, a full mesh topology is practical in an ad-hoc wireless network.
On 29 October, 2014 at 16:00 Bus topology is a form of networking where everything is connected to a central cable, referred to as the “bus”. Other connections are made in a daisy chain off of the bus cable. It is commonly used because of how simple and effective it is.
Point-to-point [ ]. Main article: The simplest topology with a dedicated link between two endpoints. Easiest to understand, of the variations of point-to-point topology, is a point-to-point that appears, to the user, to be permanently associated with the two endpoints. A child's is one example of a physical dedicated channel. Using or technologies, a point-to-point circuit can be set up dynamically and dropped when no longer needed.
Here you will see a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN). This is an extensive network which occupies a large territory including a few buildings or even the whole city. The space of the MAN is bigger than LAN, but lower than WAN. MAN comprise a lot of communication equipment and delivers the Internet connection to the LANs in the city area.
There are two types of network topologies: physical and logical. The current diagram represents precisely a physical type of LAN topology because it refers to the physical layout of a local network equipment. Fully Connected Network Topology Diagram There are several basic topologies including bus, star, point-to-point, ring and a hybrid. Two computers can form a fully connected network topology, and as the number of network nodes increases, the network diagram gets more complicated. This type of topology is also called a full mesh.
This is called spoofing. However, we will talk about spoofing later in this series. Let’s first focus on the basics. Advantage of Bus topology: • Minimal use of the physical resources Disadvantage of the Bus topology: • A Single point of failure Imagine if the cable breaks down, none of the nodes will be able to communicate with each other.
It was created using using ConceptDraw solution for the Computer and Network diagramming. The specific of this sample campus network is its distribution. It is rather broad to embrace a big campus territory.
6) Hybrid Topology The hybrid topology is the combination of multiple topologies, used for constructing a single large topology. The hybrid topology is created when two different network topologies are interconnected. If two ring topologies are connected then the resultant topology is not the hybrid topology. On the other hand, if the ring topology is connected to the bus topology then the resulting topology is called the hybrid topology. This topology generally combines the features of the two topologies and is therefore more effective and efficient than the individual topologies.